
Some companies may classify different types of debt or different types of vendors using risk classifications. For example, a start-up customer may be considered a high risk, while an established, long-tenured customer may be a low risk. In this example, the company often assigns a percentage to each classification of debt.
Income Statement Method for Calculating Bad Debt Expenses
It may be obvious intuitively, but, by definition, acash sale cannot become a bad debt, assuming that the cash paymentdid not entail counterfeit currency. The income statement method isa simple method for calculating bad debt, but it may be moreimprecise than other measures because it does not consider how longa debt has been outstanding and the role that plays in debtrecovery. Bad debt expense and uncollectible accounts expense are often used interchangeably.
What Is an Allowance for Doubtful Accounts?
This could be due to financial hardships, such as a customer filing for bankruptcy. It can also occur if there’s a dispute over the delivery of your product or service. Every business has its own process for classifying outstanding accounts as bad debts. In general, the longer a customer prolongs their payment, the more likely they are to become a doubtful account. When your business decides to give up on an outstanding invoice, the bad debt will need to be recorded as an expense.
What is the bad debt expense allowance method? Establishing a bad debt reserve
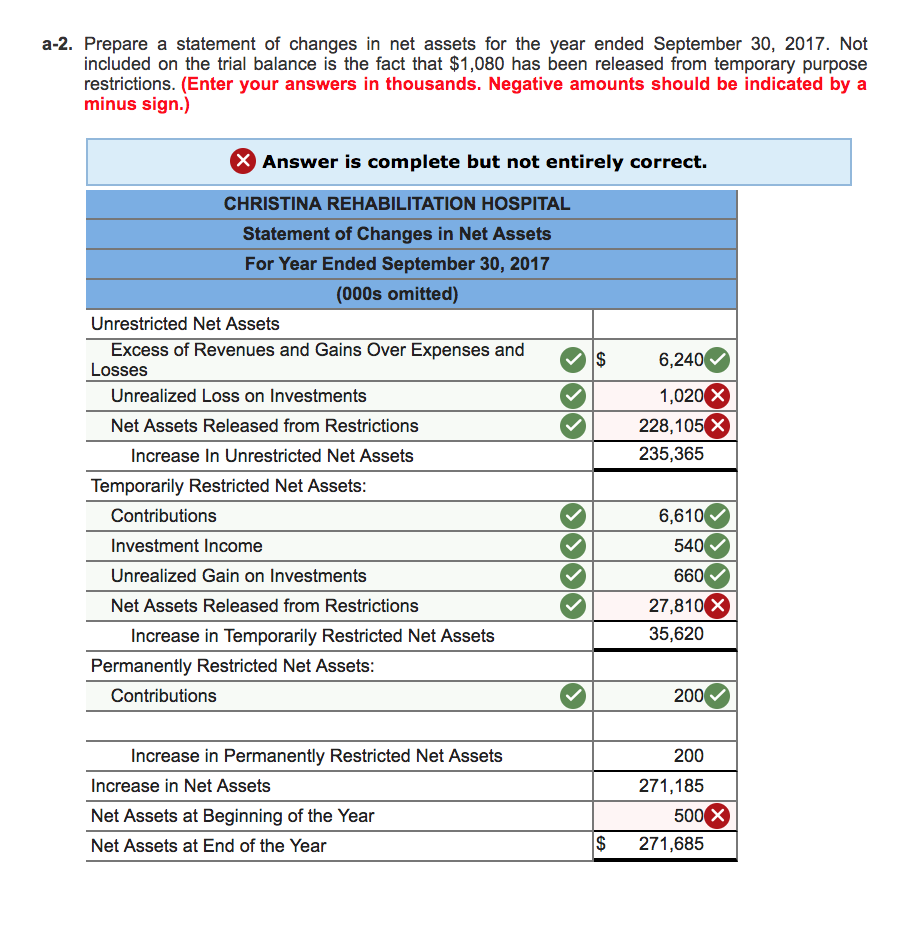
This method adheres to the GAAP matching principle by ensuring that expenses are recognized in the same period as the revenues they relate to, providing a more accurate financial picture. However, if estimates such as uncollectible accounts are consistently incorrect, management should reevaluate the method used to make the estimate. When a specific customer has been identified as an uncollectible account, the following journal entry would occur. The following table reflects how the relationship would be reflected in the current (short-term) section of the company’s Balance Sheet. As you’ve learned, the delayed recognition of bad debt violates GAAP, specifically the matching principle. Therefore, the direct write-off method is not used for publicly traded company reporting; the allowance method is used instead.
The statistical calculations can utilize historical data from the business as well as from the industry as a whole. The specific percentage will typically increase as the age of the receivable increases, to reflect increasing default risk and decreasing collectibility. Under the percentage of sales method, the expense account is aligned with the volume of sales. In applying the percentage of receivables method, determining the uncollectible portion of ending receivables is the central focus. Regardless of the approach, both bad debt expense and the allowance for doubtful accounts are simply the result of estimating the final outcome of an uncertain event—the collection of accounts receivable. This alternative computes doubtful accounts expense by anticipating the percentage of sales (or credit sales) that will eventually fail to be collected.
A bad debt expense is a portion of accounts receivable that your business assumes you won’t ever collect. Also called doubtful debts, bad debt expenses are recorded as a negative transaction on your business’s financial statements. A bad debt expense is recognized when a receivable is no longer collectible because a customer is unable to fulfill their obligation to pay an outstanding debt due to bankruptcy or other financial problems.
The Percentage of Sales Method is a straightforward approach for estimating uncollectible accounts. This method relies on historical data to determine a consistent percentage of credit sales that are expected to become uncollectible. The primary advantage of this method is its simplicity and ease of implementation, making it particularly useful for companies with steady sales patterns and predictable bad debt rates. The Percentage of Sales Method estimates bad debt expense as a percentage of total credit sales for a given period. This approach is based on historical data and trends, assuming that a consistent proportion of sales will become uncollectible over time.
- Theallowance for doubtful accounts is a contra assetaccount and is subtracted from Accounts Receivable to determine theNet Realizable Value of the Accounts Receivableaccount on the balance sheet.
- These initiatives led to a 25% improvement in the company’s accounts receivable turnover ratio and a significant reduction in bad debt expense.
- Not only does it parse out which invoices are collectible and uncollectible, but it also helps you generate accurate financial statements.
- The journal entry for allowance for doubtful accounts involves debiting the bad debt expense account and crediting the allowance for doubtful accounts account.
- This approach is income statement oriented in that it is designed to match the main expense of extending credit with the revenue produced by that activity.
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) are a set of accounting standards, principles, and procedures that companies in the United States must follow when preparing their financial statements. GAAP is designed to ensure consistency, transparency, and comparability of financial information across different organizations. As we have seen, reasonable errors in a prior year’s estimates are adjusted in current and future years; the accountant does not retroactively change a prior year’s statement.
So, an allowance for doubtful accounts is established based on an anticipated, estimated figure. The entries to post bad debt using the direct write-off method result in a debit to ‘Bad Debt Expense’ and a credit to ‘Accounts how to calculate uncollectible accounts expense Receivable’. There is no allowance, and only one entry needs to be posted for the entry receivable to be written off. The first step in accounting for the allowance for doubtful accounts is to establish the allowance.
This paints a more accurate picture of your company’s financial health — for your sake and the sake of investors. Before you can begin tackling your percentage of sales and building accurate estimations for potential investors, you need to know what allowance needs to be set for doubtful accounts. This crucial part of financial forecasting allows you to predict how your company will do next year, as it’s easy to look at sales figures, like total sales, and think your company is making X amount. In reality, you could have numerous delinquent accounts and long-term debt impacting your actual cash flow. This result is compared to the preadjustment balance in the allowance account, and the change is recorded in an adjusting entry. Calculating your bad debts is an important part of business accounting principles.


 Ассортимент игровых машин в лучших игорных заведениях с акциями
Ассортимент игровых машин в лучших игорных заведениях с акциями
Leave a Comment... Discuss!